 はじめまして!スマートバンクでサーバーサイドエンジニアをしているhiroteaです。
はじめまして!スマートバンクでサーバーサイドエンジニアをしているhiroteaです。
今回はRails ActiveRecordでCTIをサポートする、DelegatedTypeについてのご紹介です!
代表的なクラス継承パターンとして、STI、CCI、CTIなどがあげられます。Railsは標準で単一テーブル継承 (Single Table Inheritance: STI)実装をサポートしていますが、クラステーブル継承(Class Table Inheritance: CTI)の実装は困難でした。DelegatedTypeは、このCTI実装を容易にする機能であり、Rails 6.1から利用可能です。
大変魅力的な機能にも関わらずドキュメントが少なく実装にも苦労した箇所も多かったため、実装方法などを丁寧に解説しました。これから導入を考えていらっしゃる方のサポートになれば幸いです。
delegate (委譲)についても簡単に
初めに、Railsにおけるdelegateについて簡単に触れておきます。
delegateはActive Supportで提供されている機能であり、任意のオブジェクトへメソッドを移譲できるマクロです。
例えば以下のようなHabitat modelとAnimal modelを考えます。
# app/models/habitat.rb class Habitat < ApplicationRecord belongs_to :animal end # app/models/animal.rb class Animal < ApplicationRecord has_one :habitat delegate :climate, to: :habitat ## delegate(委譲)している end
以下のようなレコードを作成した場合
animal = Animal.create(name: 'Lion') habitat = Habitat.create(climate: 'Savanna', animal: animal)
Animal modelで climateをHabitatにdelegateしているため、以下のような書き方が可能です。
puts animal.climate # Output: "Savanna" ## animal.habitat.climateと同義
DelegatedTypeとは?
ではいよいよDelegatedTypeについてです。
ActiveRecord::DelegatedTypeの概要
- ActiveRecordによりクラステーブル継承(Class Table Inheritance: CTI)をサポートする。
- 委譲(delegate)により継承を表現し、シンプルな追加実装でCTIを導入できる。
- Rails6.1から利用可能
- Document: ActiveRecord::DelegatedType
- PR: Add delegated type to Active Record by dhh · rails/rails
導入方法
今回は以下のような架空のクラスを仮定し、コードサンプルとともにご紹介します。
Foodをスーパークラスとし、食材ごとのサブクラスが存在します。各サブクラスは固有フィールドをいくつか持っています。
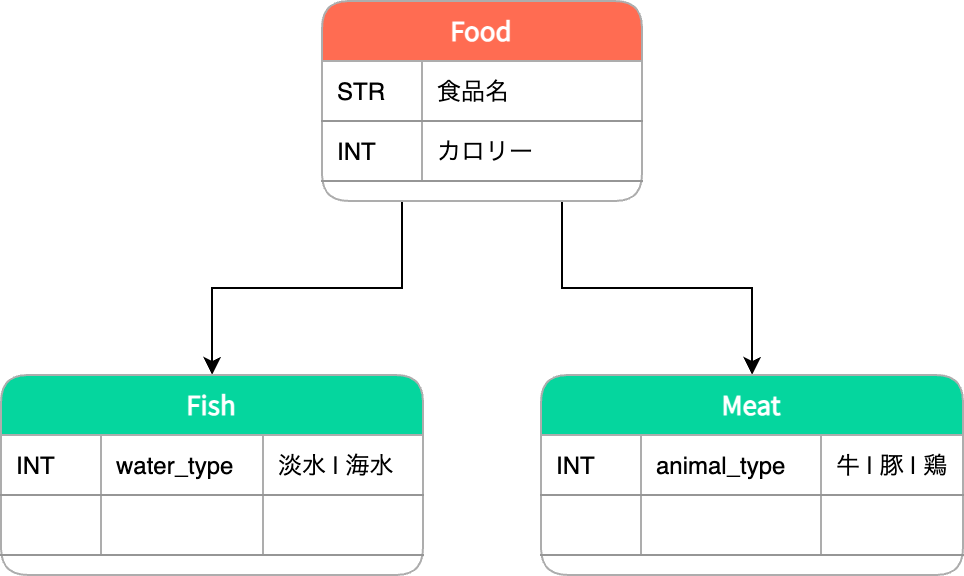
初めにfoodsテーブルにポリモーフィック関連付けで利用されるreferenceを追加します。
# db/migrate/XXXX_add_foodable_to_foods.rb class AddFoodableToFoods < ActiveRecord::Migration[7.0] def change add_reference :foods, :foodable, polymorphic: true, index: true end end
migrationを実行するとfoodsテーブルにはfoodable_typeとfoodable_idの2カラムが追加されます。
create_table "foods", force: :cascade do |t| t.string "name" t.string "foodable_type" t.integer "foodable_id" t.integer "calories" t.datetime "created_at", null: false t.datetime "updated_at", null: false t.index ["foodable_type", "foodable_id"], name: "index_foods_on_foodable_type_and_foodable_id" end
つぎに Foodable moduleを作成し、次のように記述します。
# foodable.rb module Foodable extend ActiveSupport::Concern included do has_many :foods, as: :foodable end end
抽象クラスであるFoodモデルにDelegatedTypeの記述をします。types には委譲先となる各サブモデル名を記述し、委譲先モデルクラスにmoduleをincludeします。
# food.rb class Food < ApplicationRecord delegated_type :foodable, types: %w[Meat Fish] end
# fish.rb class Fish < ApplicationRecord include Foodable ... end # meat.rb class Meat < ApplicationRecord include Foodable ... end
これで準備完了です!実際にレコードを追加して挙動を見てみます。
レコードの作成
次のように記述するだけで作成できます。
Food.create(name: 'Salmon', calories: 100, foodable: Fish.new(water_type: :seawater) ) Food.create(name:'Beef Steak', calories:600, foodable: Meat.new(animal_type : :beef))
テーブルを確認します。foods.foodable_type foods.foodable_id にそれぞれサブクラス名とidが格納されています。
- foodsテーブル.
| id | name | calories | foodable_type | foodable_id | created_at | updated_at |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Salmon | 100 | Fish | 1 | 2023-07-24 01:35:46.689559 | 2023-07-24 01:35:46.689559 |
| 2 | Beef Steak | 600 | Meat | 1 | 2023-07-24 01:35:46.689559 | 2023-07-24 01:35:46.689559 |
- fishテーブル
| id | water_type | size | weight | created_at | updated_at |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 10 | 5 | 2023-07-24 01:35:46.688463 | 2023-07-24 01:35:46.688463 |
- meatsテーブル
| id | animal_type | cut | protein | created_at | updated_at |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 20 | 2023-07-24 01:35:46.690229 | 2023-07-24 01:35:46.690229 |
レコードの呼び出し
seedデータをいくつか投入した上で、作成したレコードの呼び出し方を確認します。基本的にはFoodモデルを扱う感覚で操作できます。サブクラスモデルはFoodableとのAssociationを介して参照するイメージで操作していきます。
> food = Food.first Food Load (0.3ms) SELECT "foods".* FROM "foods" ORDER BY "foods"."id" ASC LIMIT ? [["LIMIT", 1]] => #<Food:0x000000011389d6e0 id: 1, name: "Salmon", calories: 100, created_at: Mon, 24 Jul 2023 01:35:46.689559000 UTC +00:00, updated_at: Mon, 24 Jul 2023 01:35:46.689559000 UTC +00:00, foodable_type: "Fish", foodable_id: 1>
専用のメソッドもいくつか生えています。
food.foodable_name で紐づく具象クラスを確認できます。
> food.foodable_name => "fish"
food.foodable で委譲先レコードを参照できます。
food.foodable Fish Load (0.4ms) SELECT "fish".* FROM "fish" WHERE "fish"."id" = ? LIMIT ? [["id", 1], ["LIMIT", 1]] => #<Fish:0x000000010ccdc870 id: 1, water_type: "freshwater", size: 10, weight: 5, created_at: Mon, 24 Jul 2023 01:54:34.493333000 UTC +00:00, updated_at: Mon, 24 Jul 2023 01:54:34.493333000 UTC +00:00>
Fishに紐づくレコードだけ取り出したい場合はFood.fish でOKです。
Food.fish Food Load (0.4ms) SELECT "foods".* FROM "foods" WHERE "foods"."foodable_type" = ? [["foodable_type", "Fish"]] => [#<Food:0x000000010eb471e8 id: 1, name: "Salmon", calories: 100, created_at: Mon, 24 Jul 2023 01:54:34.494446000 UTC +00:00, updated_at: Mon, 24 Jul 2023 01:54:34.494446000 UTC +00:00, foodable_type: "Fish", foodable_id: 1>, ...]
FoodモデルをActiveRecordらしく直感的に書け、学習コスト低く利用できそうであることが伝わるかと思います。
メソッドの委譲
DelegatedTypeで定義したサブクラスに対してメソッドを移譲することも可能です。
例えば食べ物ごとの説明文special_feature をモデルごとに出し分けたい場合は次のようにdelegateをFoodモデルに追記し、各サブクラスにspecial_featureを追加するだけでOKです。
# food.rb class Food < ApplicationRecord delegated_type :foodable, types: %w[Meat Fish] delegate :special_feature, to: :foodable # foodableに委譲する end # fish.rb # 他モデルも同様に追記するだけ class Fish < ApplicationRecord ... def special_feature "This fish lives in #{water_type} and its size is #{size}." end end
> Food.all.map(&:special_feature) Fish Load (0.1ms) SELECT "fish".* FROM "fish" WHERE "fish"."id" = ? LIMIT ? [["id", 1], ["LIMIT", 1]] Meat Load (0.1ms) SELECT "meats".* FROM "meats" WHERE "meats"."id" = ? LIMIT ? [["id", 1], ["LIMIT", 1]] => ["This fish lives in freshwater and its size is 10.", "This meat comes from a beef and is cut as steak."]
「Foodに対してメソッド呼び出しが走った際に特定のサブクラスモデルだけはエラーを返す」ような制御や、固有カラムを使ったsortなどに活用できます。
preloadはpreload(:foodable) で行えます。
> foods = Food.all.preload(:foodable) Food Load (0.2ms) SELECT "foods".* FROM "foods" WHERE "foods"."foodable_id" = ? [["foodable_id", 1]] Fish Load (0.4ms) SELECT "fish".* FROM "fish" WHERE "fish"."id" = ? [["id", 1]] Meat Load (0.1ms) SELECT "meats".* FROM "meats" WHERE "meats"."id" = ? [["id", 1]] => [#<Food:0x000000010eb1d3e8 ... > foods.map(&:special_feature) => ["This fish lives in freshwater and its size is 10.", "This meat comes from a beef and is cut as steak."]
実装で戸惑ったところ
- ActiveRecordらしくかけて良いこと尽くめのDelegatedTypeですが、いくつか実装時に戸惑った点もありました。
ポリモーフィック関連と同じ制約がある
- ポリモーフィック関連付けをしているため以下のようなクエリがかけません。(ポリモーフィック関連付け側の仕様なので仕方ないのですが)
- 以下のようにMeatの産地を表すCountry modelを追加して考えてみます。
# app/models/country.rb class Country < ApplicationRecord has_many :meats end # app/models/meat.rb class Meat < ApplicationRecord belongs_to :country end class CreateCountries < ActiveRecord::Migration[7.0] def change create_table :countries do |t| t.string :name t.timestamps end add_reference :meats, :country, foreign_key: true end end
- このとき
MeatとAssociationを持つCountry.name=”Japan”で絞り込んだものを取得…のようなクエリを書こうとした際、前提として以下のようなコードは書けません。
> Food.joins(:foodable) # An error occurred when inspecting the object: #<ActiveRecord::EagerLoadPolymorphicError: Cannot eagerly load the polymorphic association :foodable>
- Meatモデルを経由してCountryモデルをJoinsして…とやろうとしてもうまくいかないので、下のように書いてやる必要があります。
## 書けない > Food.joins(meat: :country).where(countries: { name: 'Japan' }) # Can't join 'Food' to association named 'meat'; perhaps you misspelled it? (ActiveRecord::ConfigurationError) ## こう書く必要がある > Food .where( id: Meat.joins(:country).where(countries: { name: 'Japan' }) )
スーパークラスとサブクラス横断クエリ
- 他にも
スーパークラスのフィールドとサブクラスのフィールドそれぞれをsort_keyとして並べ替えるような場合にも少し苦戦しました。 - 例えばFood.caloriesと、Fish、Meatそれぞれの適当なフィールドでsortするようなケースを考えてみます。一覧取得するさいにビジネスロジックで並び替えるようなケースのイメージをしていただければと思います。
- まず
sort_orderというメソッドをサブクラスに用意し、Foodからdelegateしておきます。
class Food < ApplicationRecord delegated_type :foodable, types: %w[Meat Fish] delegate :sort_order, to: :foodable end ## FishとMeatにsort_orderメソッドを追加 class Fish < ApplicationRecord include Foodable enum water_type: { freshwater: 0, saltwater: 1 } def sort_order water_type end end class Meat < ApplicationRecord include Foodable belongs_to :country enum animal_type: { beef: 0, pork: 1, chicken: 2, lamb: 3 } def sort_order animal_type end end
- こうすることでsort_byを使った並べ替えが実現できます。ActiveRecordArrayに対して操作しているため、orderは利用できません。
foods = Food.all
sorted_foods = foods.sort_by{ |food| [food.calories, food.sort_orders] }
B/43 での導入事例
引き続いて、実際のB/43での導入事例をご紹介します。今回は先日リリースされたB/43プラスのメンバーシップ限定機能である「カスタムカテゴリ」でdelegated_type を利用しました。
カスタムカテゴリとは
B/43では、これまでデフォルトの12のカテゴリ(プリセットカテゴリ)から自由に選び、明細に紐づけて管理することができました。「カスタムカテゴリ」機能は既存のカテゴリに加え、ユーザーの作成したカテゴリも同様に明細に紐づけられるようになる機能です。そのため、以下のようなクラス設計にする必要があり、スーパークラスであるカテゴリと、サブクラスであるプリセット/カスタムカテゴリの継承関係表現のためにdelegated_typeを利用しています。

CTIを採用した経緯などについては先日のB/43 tech_talkでご紹介していますので、よろしければご覧ください🐙
まとめ
Railsのdelegated_typeは、ActiveRecordでCTIをシンプルに実装できる強力な機能です。自分自身が導入時に事例が少なく、苦労したことから今回は丁寧に導入方法とポイントをご紹介いたしました。
弊社ではRailsの新機能を積極的に試しながら新機能開発に携わりたいエンジニアを募集しています!